Blog
What is an inverter?
Writer: admin Time:2022-07-05 09:00 Browse:℃
An inverter or power inverter, refers to an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). In our daily life, we often convert 110V or 220V AC power into DC power for use, while the inverter plays the opposite role. In other words, the inverter is used to convert the 12V, 24V or 48V DC power via car battery or battery bank to AC 110V, 120V, 220V, 230V, or 240V AC power. The power inverter can provide AC household power on the move, ideal for charging the electronics or appliances such as mobile phones, iPad, computers, TV, washing machines, rice cookers, refrigerators, video recorders, fans, lighting, air conditioning, electric grinding wheel, electric tools, etc. Therefore, the inverter is a must-have when you are working outside, traveling, camping or encountering emergency power failure.

Features of inverter
- High conversion efficiency and fast start-up.
- Good safety. The inverter has multiple protection functions, such as short circuit, overload, over-voltage, under-voltage, over-temperature and reverse connection.
- Good physical properties. With the aluminum shell, the inverter has good heat dissipation. With hard oxidized surface, it has good friction resistance and can resist extrusion or impact of a certain external force.
- Strong adaptability and stability with load.
Structure and principle of inverter
The power inverter is a kind of DC to AC transformer, and it is actually a process of voltage inversion compared with the converter. The converter is to convert the AC power of the mains grid into a stable 12V DC output, while the inverter is to convert the 12V DC voltage of the adapter into high-frequency high-voltage alternating current. Both of converter and inverter use the pulse width modulation (PWM) technology. The inverter is made of inverting circuit, logic control circuit and filtering circuit, mainly including input interface, voltage start circuit, MOS switch, PWM controller, DC conversion circuit, feedback circuit, LC oscillation and output circuit, load and so on, as shown in the following figure.
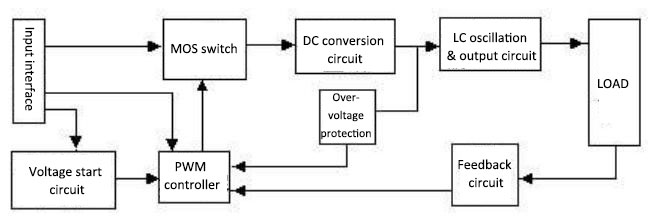
-
Input interface
The input interface includes 3 signals, 12V DC input VIN, working enabling voltage ENB and Panel current control signal DIM. Among them, VIN is provided by adapter, and ENB voltage is provided by MCU on the main board with a value of 0 or 3V. When ENB is zero, the inverter does not work, while when ENB is 3V, the inverter works normally. Meanwhile, DIM voltage is provided by the main board with a range of 0 to 5V, which feeds back different DIM values to the feedback terminal of the PWM controller. In addition, power inverter will also provide different currents to the load, the smaller DIM value, the greater output current from the inverter. -
Voltage start-up circuit
When ENB is in high level, the backlight lamp of Panel is lighted by output high voltage. -
PWM controller
It has the following functions: internal reference voltage, error amplifier, oscillator and PWM, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, short circuit protection, output transistor. -
DC conversion
Voltage conversion circuit is made of MOS transistor and energy storage inductance. The input pulse is amplified by push-pull amplifier to drive the MOS transistor to switch on or off, so that the DC voltage charges and discharges the inductor, and the other end of the inductor can obtain AC voltage. -
LC oscillation and output circuit
It can ensure the 1600V voltage required to start the lamp and reduce the voltage to 800V after the lamp is started. -
Output voltage feedback
When the load is working, the sampling voltage is reflected to stabilize the voltage output of the inverter.
In brief, the control circuit of the inverter controls the operation of the whole system, the inverting circuit plays role of converting direct current into alternating current, and the filtering circuit is used to filter out undesired signals. The more specific work of the inverting circuit is as follows: firstly, the LC oscillation circuit converts DC power into AC power; secondly, the coil steps up the irregular alternating current into a square alternating current; finally, the square alternating current is rectified to sine wave alternating current.